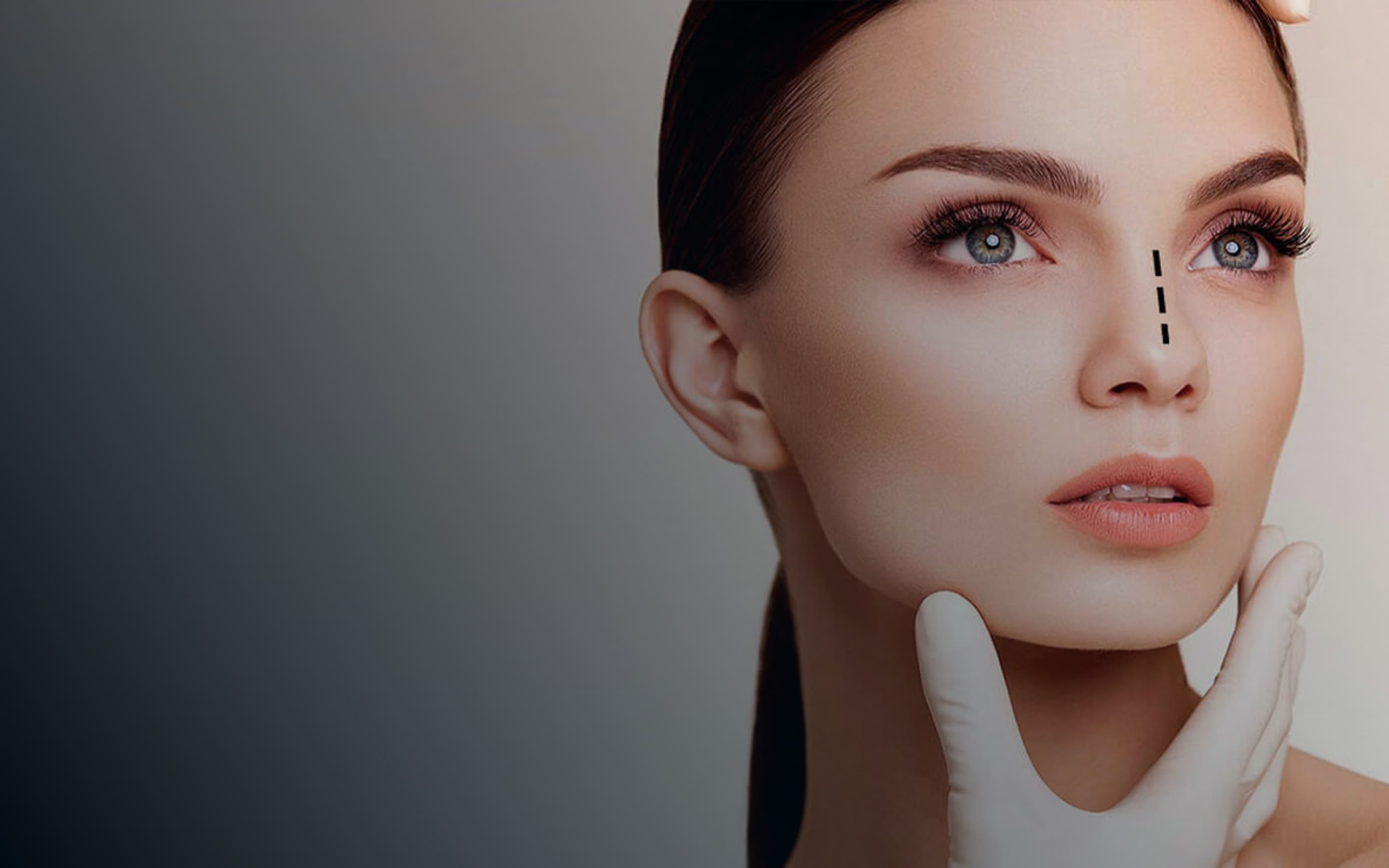
Rhinoplasty
What is it?
Rhinoplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at changing the shape, size, or functionality of the nose.
The indications for rhinoplasty can be both medical and aesthetic. Most often, the procedure combines these two aspects.
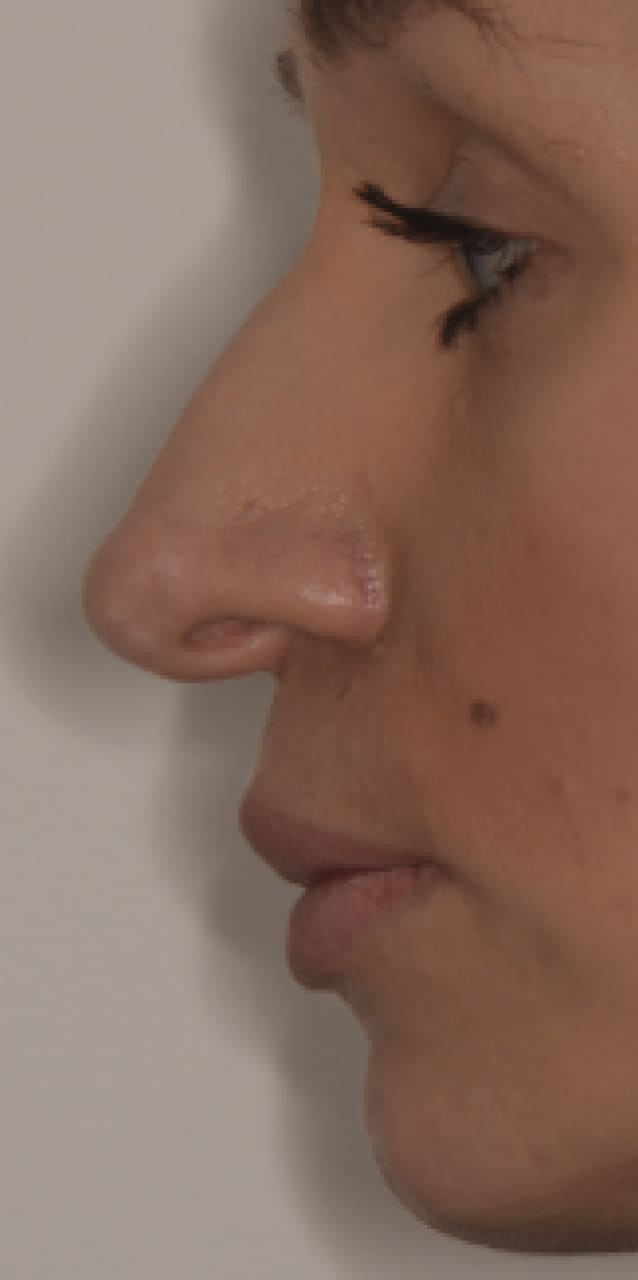
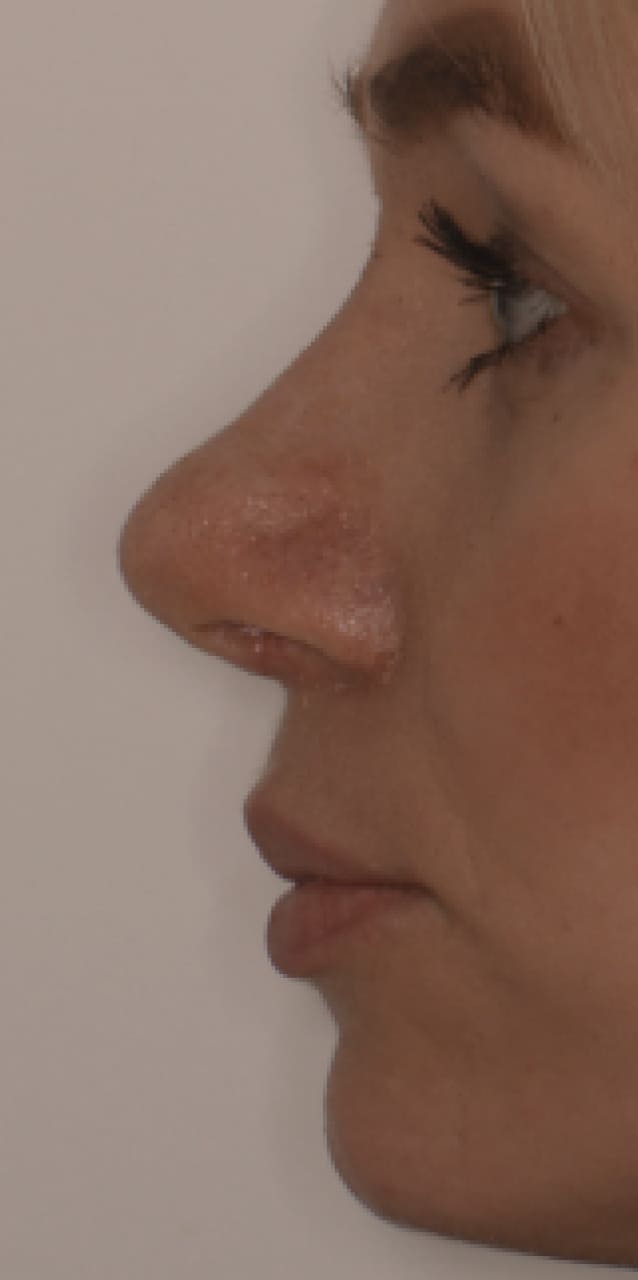
Rhinoplasty is performed for:
The nose is too large or small compared to other facial features
Hump on the bridge of the nose
Square, round, or asymmetrical nose tip
Wide or narrow nostrils.
Consequences of fractures or other injuries that disrupt the shape or function of the nose
Scar changes after injuries or surgeries.
Deviated nasal septum
Narrowing of the nasal passages
Chronic nasal congestion due to anatomical features.
Congenital nose deformities (cleft lip, cleft palate, etc.)
Improper development of cartilage or bone tissue.
Persistent sinus infections due to anatomical issues
Recurring nosebleeds due to curvature or other defects.
Different shapes or sizes of the nose sides
Noticeable shift of the nose from the central line of the face.
Reconstruction after unsuccessful rhinoplasty.
How is the preparation for rhinoplasty carried out?
Preparation for rhinoplasty is an important stage that helps minimize risks, ensure safe surgery, and achieve desired results.
It involves several key steps.
Discussing the patient’s expectations and determining realistic outcomes
Analyzing the shape and anatomy of the nose, assessing functional problems
Photographing the nose to plan changes and possibly perform 3D modeling of the future result
Reviewing the patient’s medical history (allergies, chronic diseases, previous surgeries, nasal injuries).
Blood tests (general, coagulation, biochemical)
Nasal examination (rhinoscopy, computed tomography) to assess the condition of nasal structures
Electrocardiogram (ECG) and consultation with a therapist to check overall health
Excluding acute infections, inflammatory processes, or chronic diseases in the acute stage.
Are there contraindications for rhinoplasty?
Yes, there are several contraindications for rhinoplasty. They can be absolute (where surgery is strictly prohibited) or relative (when surgery is possible after eliminating risk factors or under certain conditions).
Acute or chronic diseases in the acute stage: ARVI, flu, other infectious diseases, chronic diseases (e.g., bronchitis, sinusitis) in the acute phase.
Bleeding disorders: hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, or other coagulopathies.
Serious cardiovascular diseases: uncontrolled hypertension, heart failure.
Respiratory diseases: severe bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Oncological diseases: any form of malignant tumors.
Age: Rhinoplasty is not recommended before the completion of nasal bone and cartilage formation (usually up to 18 years, except for medical indications).
Smoking: it slows down the healing process, so patients are advised to quit smoking before and after surgery.
Systemic diseases: diabetes mellitus, especially in severe form (surgery is possible only with good glucose level compensation).
Skin infections: acne, dermatitis, or other diseases in the nose and face area.
Pregnancy and lactation: it is recommended to postpone rhinoplasty.
What are the surgical techniques for rhinoplasty?
This technique involves making all incisions inside the nose, leaving no external scars.
This technique involves an additional incision on the columella (bridge between the nostrils), allowing full exposure of nasal anatomical structures.
This modern technique uses ultrasonic tools to work with the bony structures of the nose.
This technique combines cosmetic nose correction with nasal septum correction (septoplasty).
Performed to correct deficiencies or complications after previous rhinoplasty. <br> It may require cartilage grafting from other areas (ear, rib).
Used to restore the shape and function of the nose after injuries, surgeries, or congenital defects. <br> Cartilage or bone tissue grafts are used.
This technique aims to change the shape or size of the nostrils without significant intervention in other nasal structures.
Uses an endoscope to perform precise manipulations in hard-to-reach areas of the nose.
Rhinoplasty can be performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia (narcosis). <br><br> The choice depends on the complexity of the surgery, the duration of the intervention, the patient's health condition, and the recommendations of the surgeon or anesthesiologist.
How is recovery after rhinoplasty carried out?
Recovery after rhinoplasty is an important phase that affects the final result of the surgery.
Recovery stages:
A splint or plaster cast is applied to the nose to fix the shape
Tampons or special silicone tubes may be placed in the nostrils to support nasal passages (removed after 1–3 days)
Swelling, bruising around the eyes, nasal congestion, and mild pain (usually controlled with painkillers) may occur
It is recommended to keep the head elevated, even during sleep (2–3 pillows), and avoid physical exertion and bending.
Plaster or splint on the nose remains for 7–10 days
Swelling and bruising gradually subside, though they may remain visible
Recommended: avoid touching the nose, excessive facial expressions, hot food, and drinks
Bruising usually disappears by the end of the second week
Swelling subsides, although the tip of the nose may remain slightly swollen
It is recommended to avoid physical exertion, intensive exercises, and saunas, as well as to protect the nose from injuries, sunlight, and sharp temperature changes
Major swelling decreases, and the shape of the nose becomes more defined
Nasal breathing is restored if there were any problems
The patient can gradually return to a normal lifestyle.
The final result of rhinoplasty becomes fully noticeable
All residual swelling disappears
Scars (if any) become less visible.
Following the doctor's recommendations and taking proper care of oneself will help ensure a successful recovery and achieve the desired result.
Rhinoplasty prices
Consultation with an otolaryngologist
1000 UAH
Computed tomography of the nose and paranasal sinuses
3000 UAH
Surgery cost
93000 UAH
Anesthesia cost
5000 UAH
Contacts
On.teodor@gmail.com
Address
Lviv, Dekarta St. 6
